In recent years, generative artificial intelligence has profoundly transformed various sectors, revolutionizing the way companies operate and tackle daily challenges. One area where this technology is starting to have a significant impact is Risk Management. Generative AI’s ability to analyze large volumes of data, recognize complex patterns, and generate new information makes it a powerful tool for identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks more effectively than traditional approaches.
The Potential of Generative AI in Risk Management
The use of generative AI in Risk Management is a high-potential solution. First, its ability to quickly process and analyze data from various sources allows risk professionals to obtain a complete and integrated view of potential dangers. Through advanced machine learning techniques, AI can identify correlations between variables that might escape human analysis, identifying emerging risks before they become critical. Additionally, generative AI can simulate hypothetical scenarios and predict the impact of different risk mitigation strategies. This allows companies to test and optimize their responses to potential crises in a virtual environment, reducing the need for costly and potentially damaging corrective actions in the future.
The 5 Fundamental Phases of the Risk Management Process
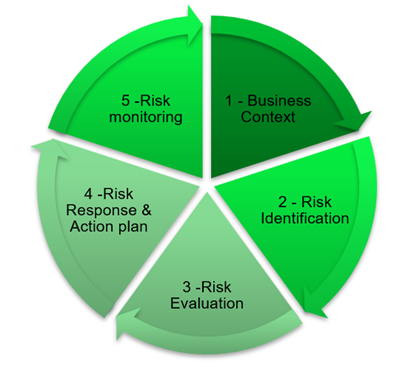
Image 1: The fundamental phases of Risk Management
The risk management process can be summarized in the following 5 key steps:
1. Business context: This phase involves understanding and analyzing the business context. It is necessary to identify the organization’s objectives, its operating environment, its stakeholders, and its resources. Understanding the context helps determine the types of risks that could impact the company’s objectives. This phase is crucial because it lays the foundation for the entire risk management process, ensuring that risk is identified and managed consistently with the company’s objectives and priorities.
2. Risk identification: In this phase, the goal is to identify all the potential risks that could negatively impact the company’s objectives. This includes gathering information from various sources, such as historical analyses, interviews, workshops, and specific analysis tools. The correct identification of relevant risks is essential to avoid unpleasant surprises in the future.
3. Risk assessment: Once the risks have been identified, they must be assessed in terms of probability and impact. The risk assessment phase consists of analyzing and classifying risks based on their severity, determining which ones require immediate intervention and which can be monitored. Risk matrices or other quantitative and qualitative techniques are often used to assess the level of probability of events and support the decision-making process.
4. Risk response & Action Plan: After assessing the risks, it is time to decide how to respond, and this phase involves developing an action plan. Responses may include avoiding, mitigating, transferring, or accepting the risk, depending on its assessment. It is important that the action plan is clear, feasible, and aligned with the organization’s available resources. This phase culminates in the implementation of preventive or corrective actions to manage risks.
5. Risk monitoring: The final phase concerns the continuous monitoring of risks and the measures taken to manage them. Monitoring ensures that risk management plans are effective and that any new risks are identified promptly. Furthermore, it allows risk management strategies to be adapted in response to changes in the business context or in the risks themselves. This phase also includes the regular review of risks and actions taken, to ensure that the organization remains prepared and resilient.
Tangible Benefits: Efficiency, Accuracy, and Proactivity
One of the main advantages of using generative AI in Risk Management is increased efficiency. AI technologies automate much of the data collection and analysis, allowing risk managers to focus on more strategic tasks. This reduces the time required to identify and assess risks and improves the accuracy of forecasts and decisions.
Another strength is proactivity. While traditional approaches to Risk Management tend to be reactive, AI’s ability to anticipate potential risks allows companies to take preventive measures, reducing the likelihood of adverse events.
Criticisms and Challenges in Adopting AI
Despite the many benefits, the adoption of generative AI in Risk Management is not without challenges. One of the main criticisms concerns data quality. The effectiveness of AI depends heavily on the quality and quantity of available data. Incomplete, inaccurate, or outdated data can lead to incorrect predictions and potentially risky decisions.
Another crucial aspect is transparency. AI algorithms, especially advanced ones like deep neural networks, are often considered “black boxes,” meaning processes whose internal workings are difficult to fully understand. This can raise concerns about trust in decisions made by AI, especially in a sensitive field such as Risk Management.
Finally, there is the issue of compliance. The use of generative AI must comply with existing regulations on risk management and data protection. Companies must ensure that the implementation of these technologies respects applicable laws and regulations, thus avoiding potential penalties or damage to reputation.
Comparison with Traditional Approaches
Compared to traditional approaches, which often rely on manual analysis and static statistical models, generative AI offers unprecedented flexibility and adaptability. While traditional methods can take weeks to process and analyze large volumes of data, AI can do so in minutes, providing timely and useful information for risk management.
However, AI should not be considered a complete replacement for traditional approaches. On the contrary, the combination of human experience and the capabilities of generative AI can be the winning strategy. Risk professionals can use AI as a complementary tool that enhances their analyses and decisions, rather than replacing them.
In essence, companies that are able to combine the efficiency and proactivity offered by AI with human experience and judgment will have a significant competitive advantage, ready to face the challenges of the future with greater security and resilience.
Authors: Andrea Fiore and Alfonso Russo | DMBI Data Scientists
Photo by Jandira Sonnendeck on Unsplash





